Understanding Vitamin B12 and Folate
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is a water soluble vitamin that is naturally
present in some foods. It is a nutrient that helps keep the body’s nerve and
blood cells healthy and helps make DNA, the genetic material in all cells.
Vitamin B12 also helps prevent a type of anemia called megaloblastic anemia
that makes people tired and weak. Vitamin B12 is required for proper red blood
cell formation, various neurological functions, as well as DNA synthesis.
Vitamin B12 functions as a cofactor for many crucial enzymes.
Vitamin B12 is found in various animal products such as
fish, meat, poultry, eggs, milk, and milk products. Vitamin B12 is generally
not present in plant foods. Some nutritional yeast products contain B12. In
food sources, Vitamin B12 is founds as cyanocobalamin, a form that the body
needs to convert into the active forms of methylcobalamin and
5-deoxyadenosylcoabalamin.
Vitamin B9 (Folate)
5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) is the most biologically
active form of the B-Vitamin folic acid, also known generically as folate,
5-MTHF functions, in concert with vitamin B12, as methyl-group donor involved
in the conversion of the amino acid homocysteine to methionine, methyl group
donation is vital to many bodily processes, including serotonin, melatonin, and
DNA synthesis. Therapeutically, 5-MTHF is instrumental in reducing homocysteine
level, preventing neural tube defects and improving vascular endothelial
function.
Furthermore, certain neurological, cognitive, and
psychiatric presentations may be secondary to folate deficiency. Such
presentations include depression, peripheral neuropathy, myelopathy, restless
legs syndrome, insomnia, dementia, forgetfulness, irritability, endogenous
depression, organic psychosis, and schizophrenia-like syndromes. 5-MTHF
supplementation may be a more favorable method of folate repletion.
Vitamin B12 along with folate (vitamin B9) is essential for
the production of red blood cells and aids in the maintenance of a healthy
nervous system and immune system. B12 deficiency damages the fatty
tissue-myelin-which surrounds and protects nerve fibers. It damages the brain,
spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and nerves of the eye. It is a crucial element
in the construction of DNA.
Low levels or deficiency of Vitamin B12 and Folate have
serious effects on health. This may result in negative clinical manifestations
such as elevated levels of homocysteine, anemia, psychiatric disorders like
depression, and cardiovascular diseases.
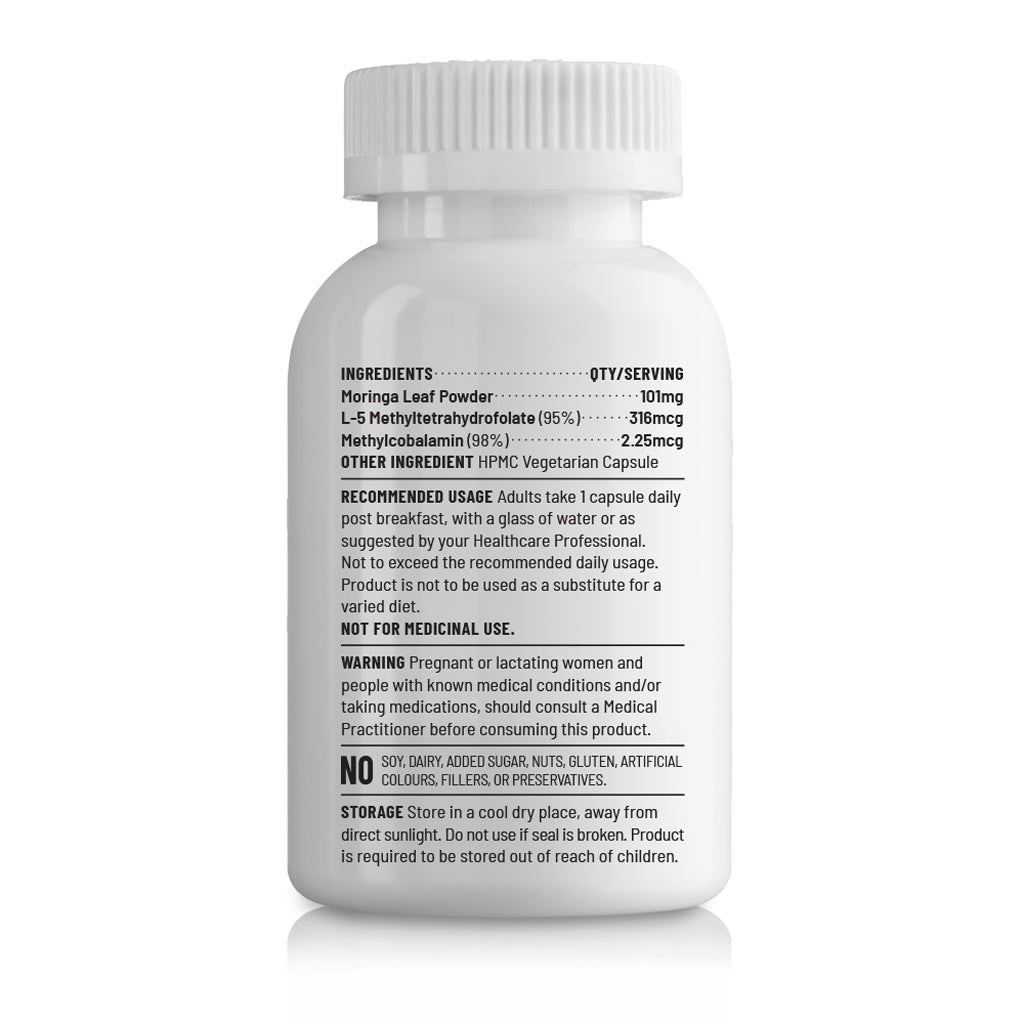
Our Formulation
Unived’s B12-Veg is a formulation of active vitamin B12
(methylcobalamin) with 98% purity and active vitamin B9
(5-methyltetrahydrofolate).
Mode of Action:
Vitamin B12
B12 works with the B vitamin folate to produce DNA – body’s
genetic material.
- Helps keep levels of the amino acid homocysteine in check,
which may help decrease heart disease risk. - Forms new red blood cells through proliferation of
erythroblasts (immature red blood cells). - Aids in tissue growth and plays a role in cellular
respiration and energy. - Allows the body to use certain nutrients.
- Facilitates numerous chemical reactions.
Vitamin B9
- The mode of action of 5-MTHF is through its role as a methyl
donor in a range of metabolic and nervous system biochemical processes as well
as being indirectly necessary for DNA synthesis. 5-MTHF donates its methyl
group to cobalamin (vitamin B12) forming methylcobalamin. Methylcaobalmine then
converts homocysteine into methionine. Methionine subsequently is converted to
S-adenosyl methionine (SAMe), a methyl donor involved in numerous biochemical
processes.



 Sold outVendor:Daily Energy Bundle
Sold outVendor:Daily Energy Bundle




